What the FBI Internet Crime Report Tells us on Email Security

Cybercrime broke new records in 2021 with a 68% increase in the number of reported data breaches and 148% more ransomware attacks compared to 2020. These are just some of the figures that illustrate the severity of the threat and help raise awareness of the problem.
Another comprehensive resource for observing the state of cybercrime in the United States is Internet Crime Report 2021 by the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3). As a division formed to “provide the American public with a direct outlet to report cybercrime to the FBI”, IC3 has immediate insights into online users’ cybercrime complaints. Its yearly reports are intended to identify ever-evolving trends and help create a safer cyber landscape.
The 2022 edition analyses 847,376 total complaints received last year, providing a detailed overview of fraudulent activities and associated financial losses. This article outlines its key findings.
Top 5 Internet Crime Types
Established in May 2000, IC3 has been receiving an average of 552,000 complaints per year, totaling 6.5 million so far. Such a comprehensive corpus helps paint a realistic picture of the state of cybercrime and identify critical systems, user groups, and online activities leading to data breaches.
Below is a list of the most dominant threats in 2021:
- Phishing/Vishing/Smishing/Pharming – with a total of 323,972 complaints received, phishing emails remain the most common online threat.
- Non-Payment/Non-Delivery – a scam where users don’t get paid for items they shipped or do not get items they paid, follows phishing with a significantly lower number of reported breaches – 82,478.
- Personal Data Breach – like most other crime types, personal data breaches have significantly grown compared to the previous year (51,829 in 2021 vs. 45,330 in 2020).
- Identity Theft – similar to Personal Data Breach, Identity theft has been reported over 51,000 times.
- Extortion had significantly fewer reports than the other threats and is the only activity except for Non-Payment/Non-Delivery which recorded a decrease compared to the previous year (39,360 in 2021 vs. 76,741 in 2020).
2021 Threats Overview
In addition to providing stats on the most common Internet Crime Types, the report also gives a detailed overview of specific frauds.
Business Email Compromise
Business Email Compromise (BEC) is a type of email fraud in which an attacker impersonates a personal contact or a business entity in an attempt to trick an online user into sending them money or sensitive information.
The attacker usually starts by compromising the email account of a targeted individual within the organization. This account is then used to send phishing emails to other employees with the aim to gain access to additional accounts or company finances.
BEC attacks are often difficult to detect and can have devastating financial consequences for businesses. Some of the examples of a BEC attack include the following:
- A fraudulent email coming on behalf of the company’s CFO asking an employee to transfer funds to an account controlled by the criminal.
- A supplier that you regularly deal with sends an invoice with an updated or unusual email address.
- A property owner receives an email from his real estate agency instructing him to send money through a wire transfer.
According to the IC3 report, BEC schemes have been reported 19,954 times and accounted for nearly $2.4 billion lost. One of the reasons quoted for the increase in these complaints is the massive shift to remote or hybrid work due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The growing use of virtual communication tools and meetings contributed to the rise of newer BEC/EAC schemes that instructed victims to send wire transfers.
Ransomware
Ransomware is malicious software that uses known vulnerabilities to access a computer system and lock users’ data. Once the data is locked, the attacker asks for a ransom to be paid in order to give the data back. The victim can be either an individual or an organization, with the latter being more prevalent.
In 2021, the IC3 received 649 ransomware complaints. The total loss due to these complaints was $49.2 million.
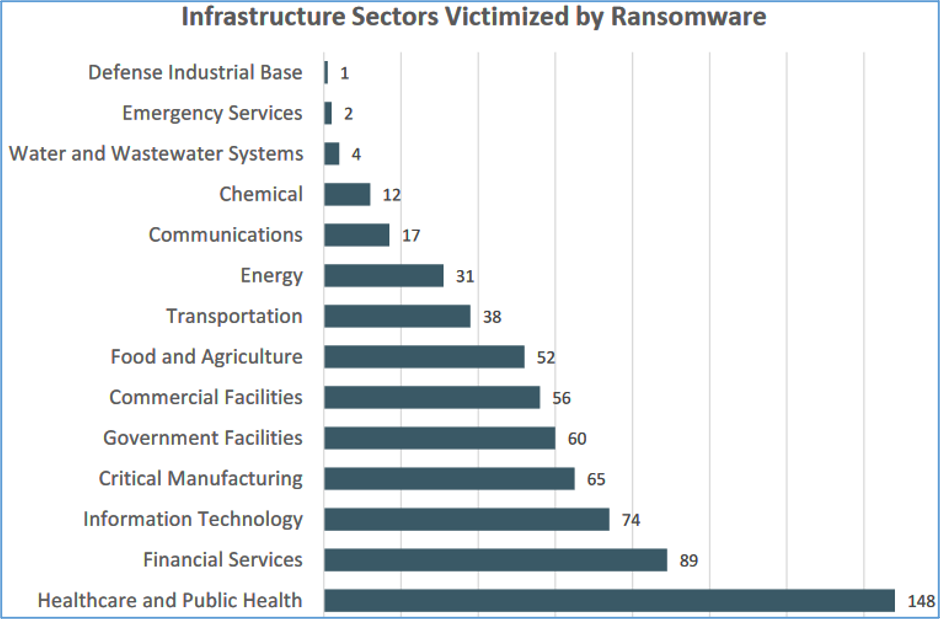
Also, out of 16 industries reporting such cases, 14 of them had at least 1 member of staff that fell into the trap of a ransomware attack.
With ransomware attacks continually evolving, organizations need more sophisticated data protection methods. The most efficient ones are listed below:
- Keep your mobile phone and laptop updated with the latest software.
- Secure your Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) to prevent third parties to gain control over your device remotely.
- Back up your critical data regularly. For businesses, this means storing at least three different copies of data in different forms (tape, cloud, and on-site).
- Have a disaster recovery plan. This is essential for organizations to ensure continuity of operations in case of a breach. A disaster recovery plan outlines all activities that need to be carried out in order to recover data.
The healthcare and public health, financial services, and information technology sectors were the industries most targeted by ransomware in 2021. IC3 expects this trend to continue in the coming years.
Phishing/Pharming
Phishing and Pharming are both types of cyber-attacks that can be used to steal sensitive information such as login credentials and credit card numbers.
Phishing is a fraudulent email that looks like it is coming from a legitimate source, such as your bank or a website you frequently use. The email typically contains a link to a fake website where a recipient is asked to enter personal information.
Pharming is similar to phishing, with the attacker using malicious code instead of an email to redirect you to a fake website.
Both phishing and pharming can be used to steal your personal information, and $44,213,707 were lost in 2021 due to both. The number of victims of phishing/pharming rose to 323,972, which was the highest among all other categories of cybercrime.
Tech Support Fraud
Tech Support Fraud involves a malevolent actor calling people, typically consumers rather than businesses, and posing as a representative from a technical support team.
It is an increasingly common type of scam in which criminals impersonate legitimate tech support representatives to gain access to victims’ computers or personal information. Fraudsters typically contact their victims by phone, and they may also use pop-up ads or websites to lure victims into contacting them.
They may claim that your computer is infected with a virus or that it needs a software update to justify asking you for your system access credentials. Once they obtain them, they can install malware or steal sensitive information such as passwords or financial details.
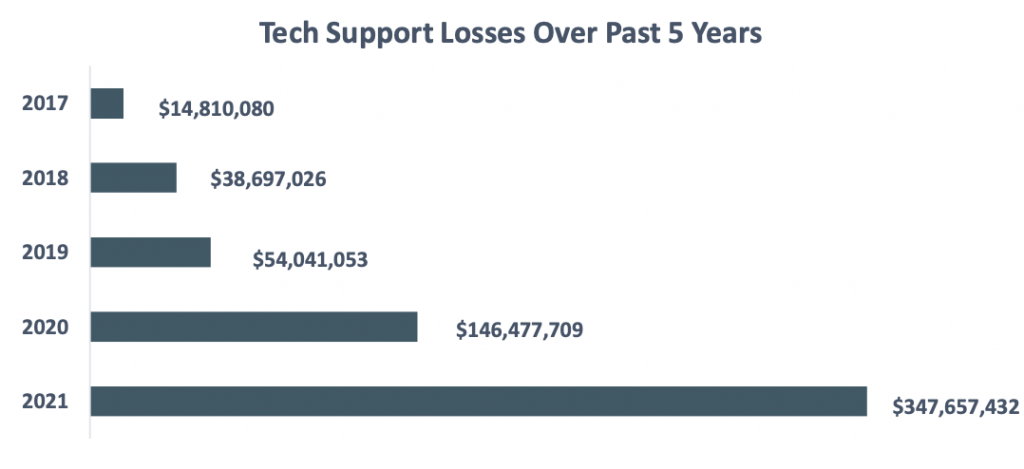
According to the 2021 FBI report, the Tech Support Fraud financial losses were $14,810,080 in 2017, and this amount increased dramatically to $347,657,432 in 2021.
Things to Remember
Hackers use sophisticated tactics to get unauthorized access to online users’ data and no one on the Internet is safe. By following recommended best practices for securing your data and your systems, you can minimize the risk of having your data breached or stolen.
This is particularly important for businesses, which risk losing thousands of dollars in a single breach. Additional consequences include productivity loss and reputational damages, which may require long-term recovery. To ensure data security and customers’ trust, companies need to use advanced access control, backup, and disaster recovery systems. In addition to this, online businesses should use robust anti-spam protection to minimize the number of fraudulent emails they receive.
Avoiding the use of public WiFi, predictable username/password combinations, and outdated software are the basic steps for individuals to protect themselves online. In addition to this, everyone should be trained to recognize suspicious emails and report anything that looks like spam to authorities.
Conclusion
The FBI Internet Crime Report is a yearly report that takes a look at different types of internet-related crimes and their prevalence. The 2021 issue provides insight into key online trends and behaviors that should help us understand the extent to which this threat has evolved in recent years. Looking at the stats from the report, it is evident that everyone needs to take steps to protect.
